It has been repeatedly written and said that osteochondrosis of the neck, neck and lumbar region is not a disease in itself. If you want, this is our "kind of curse. "Man, as a biological species, has been moving on two legs for about a few million years, or even less. This is still "the middle of the road" in terms of evolution. It is unknown what new anatomical variants of spinal development we will come to in a million years.
Osteochondrosis is currently the most common disease of the musculoskeletal system, and doctors of various specialties face it. Often these are therapists and neurologists, as complications of osteochondrosis can lead to a variety of neurological syndromes, which will be discussed below.
Osteochondrosis - what is it?

You shouldn't say, "Osteochondrosis happens often, " because that's not true. Osteochondrosis in its purest form is the process of normal aging and dehydration of the intervertebral discs, which in the normal course does not cause any complaints. This is possible in strong older people who are active, in good posture and free from excess weight. They practice gymnastics, swim, avoid heavy loads, and lead what can be called a "healthy lifestyle. "
If we talk about osteochondrosis of any part of the spine as a disease, then we always mean its complex course, which leads to various complaints and symptoms. And in this case, the cervical spine is more sensitive than other, major departments. Of course, the cervical region has the least load - only the head, but at the same time, the vertebrae of the cervical region are more mobile than others and at the same time less massive.
All this makes the lesions of the cervical region more pronounced with complications of osteochondrosis. Proximity to the head causes headaches, which, of course, does not occur with lesions of the lumbar region. In addition, it should be remembered that the spinal cord, which absorbs all the major pathways, passes through the central canal of the cervical vertebra. Therefore, a patient with central duct compression syndromes can cause complete immobility, decreased sensitivity of the skin throughout the body, and paralysis of the arms and legs to pelvic organ dysfunction. All of this can now paralyze a person, for example, with a fracture of the cervical vertebrae (diving in small places in unfamiliar places).
Of course, such complex injuries are not associated with osteochondrosis: patients are more concerned with other symptoms. How to treat and cure osteochondrosis of the cervical spine? It is impossible to cure it. To do this, as a child, simply give up moving on two legs and crawl on all fours or live in the ocean like dolphins. Only then will the load on the intervertebral discs be minimal or even disappear.
Only exacerbations of osteochondrosis can be treated, and it is necessary to know not only their signs and symptoms, but also risk factors.
About risk factors
In the case of the cervical spine, obviously, lifting weights over the shoulder will not play such an important role in the development of pain syndrome as in the lumbar region. What conditions and diseases can contribute to the development of symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis? The most common situations are:
- Straight legs, both longitudinal and transverse. The spine is a flexible, curved rod. If the arch of the foot is not moistened and there is a blow, not a "elastic" movement of the spine during the step, this blow rises with a "wave" like a whip. , and in the cervical region, the craniovertebral junction is precisely switched off. All the energy goes there. Therefore, running with straight legs causes obvious changes in the intervertebral discs.
- Chronic injury. These include, in the first place, slipping on the ice in winter, falling on the back of the head, as well as the constant hitting of the head on the low doorways, which are common in people with above-average height.
- Wear heavy winter hats, high hairstyles and lots of jewelry for women. All this leads to fatigue of the neck muscles, their chronic spasm, circulatory disorders, the development of headaches and back pain.
- Sedentary lifestyle, "sedentary" work, upper thoracic and neck stiffness.
We will not list the specific risk factors that occur in sick patients. There are many reasons for the deterioration of the situation in ordinary, healthy people.
Symptoms and signs of osteochondrosis
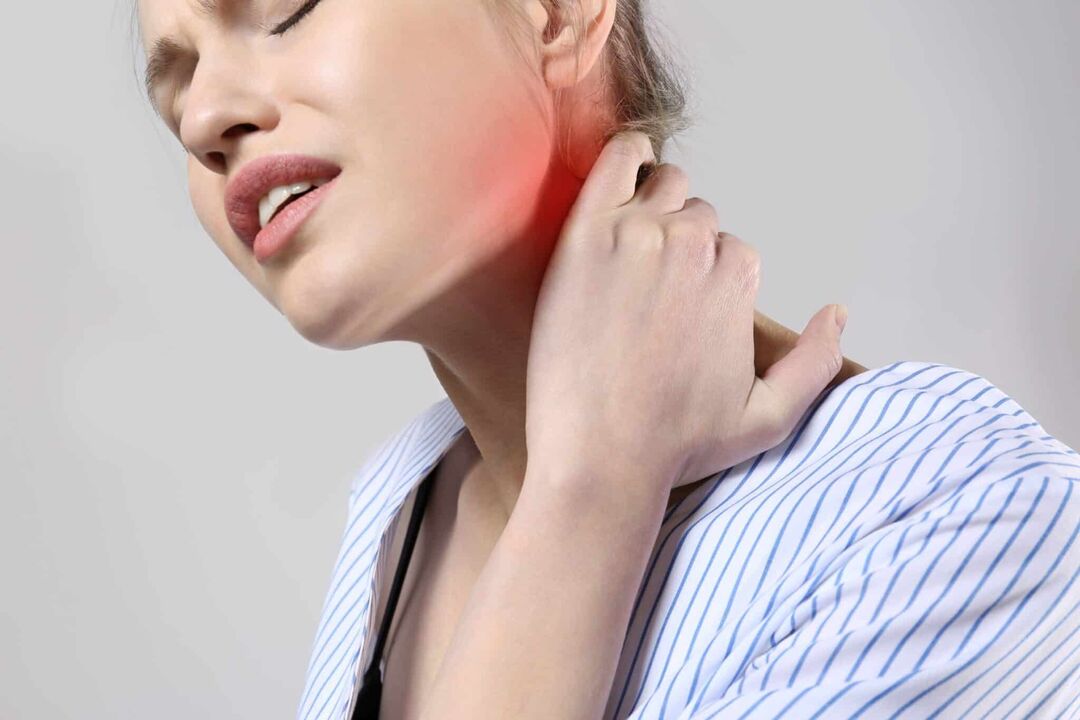
The symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine are multifaceted. Even a few doctors know that hepatic prolapse, often diagnosed as generalized prolapse of the abdomen (splanchnoptosis) or often mistakenly enlarged, may be associated with osteochondrosis of the cervical region. At this time, the phrenic nerve is irritated and the dome of the diaphragm shrinks and falls.
As a result, the liver is "pushed" out of the hypochondrium. But there are other, more "ordinary" symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis - pain and muscle tension. We will not talk about the symptoms of cervical spine hernias and protrusions - a separate article is dedicated to this. Let's talk about the clinic, which occurs with "all" intervertebral discs, especially when such cases are more common.
Cervical osteochondrosis causes pain in the neck. Muscle aches are manifested by constant, excruciating pain of low intensity. It is aggravated by turning and tilting the head. Often accompanied by stiffness in the suboccipital region.
Headaches in osteochondrosis of the cervical region are almost always a tension headache. The attack lasts for hours and even days. The pain rises from the neck through the occiput to the temples and covers the skull like a helmet or helmet. The ability to work with this pain does not suffer, but if the radicular symptoms join it, it becomes feverish and the movement of the head becomes very painful.
"Vertebral artery" syndrome
When talking about cervical osteochondrosis, it is necessary to mention this classic manifestation of cerebrovascular insufficiency caused by cervical osteochondrosis. Its symptoms are vomiting and nausea, dizziness and imbalance. There is noise in the head and ears (tinnitus), in severe cases, speech disorders (dysarthria), swallowing disorders. More often there are various visual disturbances ("flies"), headaches. Sometimes there are falls - attacks, during which a person does not lose consciousness, but falls, and then quickly rises.
Compression of one of the two vertebral arteries may occur during sleep. If a person throws his head back at the same time and turns to one side, then the vertebral artery is pressed against the first vertebra - the atlas, ie from the opposite side.
If you lie down for a while, then when you try to get out of bed in the morning, you experience severe dizziness, nausea, vomiting, gait and imbalance. In some cases, "higher-grade" disorders also develop - such as transient amnesia, in which the patient simply does not remember anything.
Numerous neurological syndromes and symptoms also arise, which we will briefly list by showing their reference diagnostic points, so that the reader of the article can imagine and "test" these symptoms for himself when he is unable to consult a neurologist:
- Lower oblique muscle syndrome of the head (often occurs in patients over 50 years of age, especially in postmenopausal women). There are pains, sensations in the back of the head, up to the auricle. The pain is painful both in the neck and in the back of the head, breaking, persistent, and its intensification is associated with prolonged inactivity. It grows by turning its head to the healthy side;
- Scalenus anterior syndrome - manifests itself in patients with additional "cervical ribs".
There are sensations of sensitivity and "crawling" in the hand, its whitening and coldness, sometimes swelling of the hand, the appearance of weakness, malnutrition of the muscles of the hand, as well as weakening of the pulse in the wrist. In severe cases, progressive paralysis or paresis of the arm muscles may occur. Patients are unable to drive, lie on the painful side, lift weights, or raise their arms (hang curtains, plaster). There are also complaints of stiffness and pain in the neck, forced head position in the morning.
- Medium scale muscle syndrome. At first there is pain in the shoulder, back, and then there begins muscle malnutrition. The mechanism is associated with damage to the long nerve of the trunk and the transverse artery of the neck;
- Shoulder-costal syndrome (scapular levator ani levator syndrome). First, there are excruciating pains in the "buzzing" back area. They give it to the shoulder, there is pain in the neck, it often hurts "in the air". A squeak is usually heard while moving the scapula.
Thus, it is clear that many processes that begin in the neck or in the immediate vicinity of its structures are seen in the "periphery", for example, in the region of the hand. This requires a thoughtful and competent approach from the doctor. At present, the diagnosis of complications of osteochondrosis has been greatly simplified, especially with the application of MRI in clinical practice.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Modern therapy for cervical vertebrogenic and associated compression and muscle syndromes involves short courses of medication. Treatment of exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the cervical region quickly turns into a pale exacerbation, against which the main treatments are kinesiotherapy and physiotherapy.
Ointments and medicines for exacerbations
As you know, "needles", ointments and even blockades have not been abolished. However, the neck is the focus of many nerves, blood vessels, autonomic fibers, and fascia. Therefore, blockades are less common here than acute pain in the back or lumbar region. In addition, the thin skin on the neck allows gels, creams and ointments to be absorbed faster than the waist area.
Injectable forms of NSAIDs, preferably selective, centrally acting muscle relaxants, B vitamins are used.
It should be remembered that if NSAIDs are used, the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract should be protected during treatment using antisecretory drugs.
As for local treatment, there are now many ointments, gels and creams containing NSAIDs, bee and snake venom, as well as agents that cool and relieve pain. The main thing is not to use too hot ointments. They can cause high blood pressure, redness of the face, and even a hypertensive crisis in old age. It is desirable to carry out treatment with ointments prophylactically without waiting for the next exacerbation.
Shants on the collar
In the early stages, in the acute stage, it is necessary to protect the neck from unnecessary movements. Shants collars are great for this. Many people make two mistakes when buying this collar. It is not chosen for its size, so it simply does not perform its function and creates a feeling of discomfort.
The second common mistake is to wear it for a long time for prophylactic purposes. This leads to weakness in the neck muscles and only causes more problems. There are only two signs for the collar, which can be worn in their presence:
- Appearance of sharp pain in the neck, stiffness and spread of pain head;
- If you engage in physical activity between "pulling" your neck and full health at risk of complications. This includes, for example, repairing while lying under the car or washing the windows when you need to reach out and hold uncomfortable positions.
The collar should be worn for no more than 2-3 days, as wearing it longer can cause venous stasis in the neck muscles at a time when it is time to activate the patient.
Patient activation
Kinesiotherapy (movement therapy) includes therapeutic exercises, swimming. For osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, gymnastics is generally focused on the surrounding muscles, not the discs. Its task is to eliminate tonic spasms, improve blood flow, as well as normalize venous flow. This leads to a decrease in muscle tone, a decrease in the severity of pain and stiffness in the back.
In addition to massage, swimming, acupuncture sessions, orthopedic mattresses and special pillows are provided. For osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the pillow should be made of a special material with "shape memory". Its task is to relax the muscles of the neck and suboccipital region, as well as to prevent disruption of blood flow at night in the vertebrobasilar basin.
Autumn is an important stage in the prevention and treatment of household physiotherapy products and devices - from infrared and magnetic devices to the most common needle applicators and ebonite discs, which are a source of weak electric currents during massage. sick.
Then what?
Statistics show that the people of the Mediterranean, who often swim at sea and at any age, are repeatedly in good health due to diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
However, the key to preventing osteochondrosis, along with eliminating risk factors, is to put on a healthy diet that includes sour milk, plant foods, seafood, fiber, and plenty of fluids. This will slow down the process of age-related dehydration of the intervertebral discs and maintain a healthy neck and back for the most advanced years.